We all have plasma
In fact, it is part of your blood
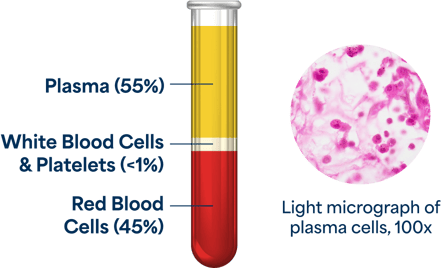
Plasma makes up about 55% of total blood volume and is composed of mostly water (90% by volume) plus dissolved proteins, glucose, clotting factors, mineral ions, hormones, and carbon dioxide. Plasma serves a variety of functions, from maintaining blood pressure to supplying critical proteins for blood clotting and immunity. Plasma contains proteins that are rich in antibodies and clotting factors.
We all have plasma
In fact, it is part of your blood
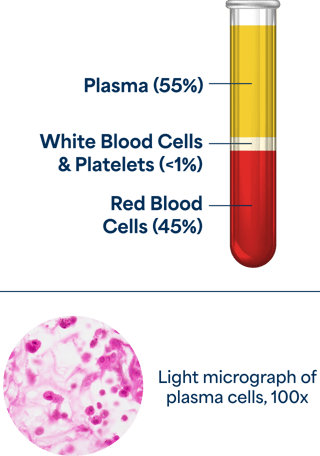
Plasma makes up about 55% of total blood volume and is composed of mostly water (90% by volume) plus dissolved proteins, glucose, clotting factors, mineral ions, hormones, and carbon dioxide. Plasma serves a variety of functions, from maintaining blood pressure to supplying critical proteins for blood clotting and immunity. Plasma contains proteins that are rich in antibodies and clotting factors.

Why Donate
People may choose to donate for different reasons:
- Donors may have a friend or loved one who can benefit from plasma derived products
- Some donors may have plasma types that contain proteins, or antibodies, specific for the treatment of rare diseases
- Plasma from donors may be used to advance important clinical research and trials designed to investigate drugs for life-threatening conditions
- Some may choose to contribute out of personal obligation or desire to help others while being compensated for their time and donation
Plasma can save lives

Immune deficiencies
This set of conditions includes those where the immune system is compromised due to a condition, a treatment, or procedure. There are over 250 types of immunodeficiency diseases. These are treated with a type of medication called “IVIG” or intravenous immune globulin. IVIG is made from combining plasma of a variety of donors. IVIG may also provide other health benefits to patients in need as well as to treat selected neuropathy patients. There are other uses for specific immune globulins and more uses being determined each day through medical research.

Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency is a hereditary lung condition in which the lungs do not have the ability to defend themselves against diseases and pollutants. Over time, the lungs become less and less able to function. This medical condition is more deadly than the emphysema caused by smoking. Plasma donors provide important proteins which enhance the lives of individuals with this condition.

Burns
Albumin is made from plasma and is used to treat burn victims, trauma patients, and individuals who experience shock.

Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a hereditary bleeding disorder. The blood of individuals with hemophilia does not clot. One of the treatments for hemophilia is Factor VIII, a protein derived from plasma.

